Optical fiber network connections use a hub and star design. The optical line terminal (OLT) device installed at the central office (called the “head end” by CATV businesses), connects to many optical network terminal (ONT) devices, the “clients”. Each connection is via an optical fiber. This design of the Optical fiber network connection is analogous to the IEEE 802.11 wireless design with a tower point to multi-point wireless access point that connects with multiple wireless client CPE’s (client premise equipment) with a broadband wireless connection. Optical fiber can provide a faster data rate than a wireless connection and is more reliable with no interference caused by the weather. The disadvantage is that an optical fiber connection installation to a home costs much more than a wireless connection to the home.
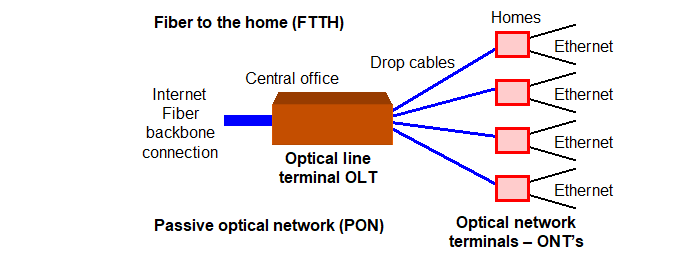
Optical fiber network design is based on a star topology. The fiber backbone is installed at the central office (called the ‘head end’ by CATV companies). The backbone connects
to the access control router and then to the optical line terminal (OLT). The OLT then connects to a fiber distribution hub using a feeder optical cable.
The fiber distribution hub is convenient for an urban environment where one central office may have several feeders to different neighborhoods. Each neighborhood has a fiber
distribution hub which connects to residences via drop-cables. Each residence has an optical network terminal (ONT - client) which converts the optical cable to Ethernet copper
cables and WiFi for the subscriber devices. A fiber distribution hub can be installed in an apartment building (multiple dwelling unit – MDU) with a fiber drop to each apartment
where the ONT is installed.
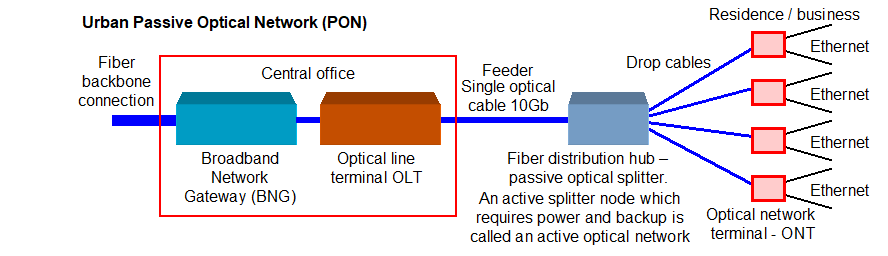
The fiber distribution hub can have a passive optical splitter (passive optical network: PON) or an active splitter (active optical network). The passive splitter requires no power,
however each drop cable is attenuated by the number of ways that the feeder is split and so the maximum distance of the fiber cable is reduced. The active optical splitter is a switch
that requires power with a backup for power outages that increases the fiber distribution hub installation and operation costs. The advantage of the active splitter is that the fiber
distances are not reduced.
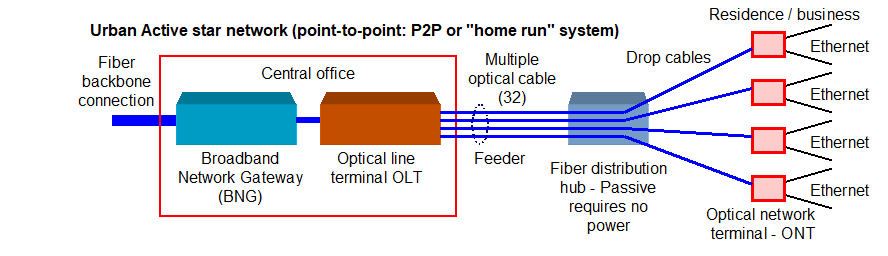
An alternative to installing a splitter at the fiber distribution hub is to connect the optical line terminal (OLT) to the fiber distribution hub with a multi-core fiber cable feeder where each fiber is allocated to a residence. The fiber distribution hub is passive and has a patch panel that connects each core of the feeder cable to an individual drop cable. In this case there is very little attenuation at the fiber distribution hub.
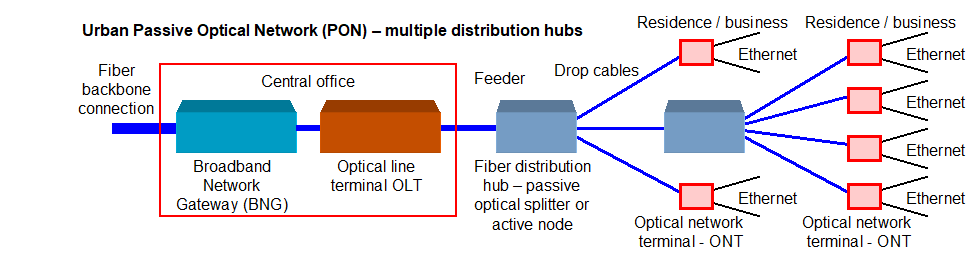
Urban networks can be expanded by connecting fiber distribution hubs in a chain to connect neighborhoods at further distances. The fiber distribution hubs will be active in order to maintain the maximum length of fiber cables.
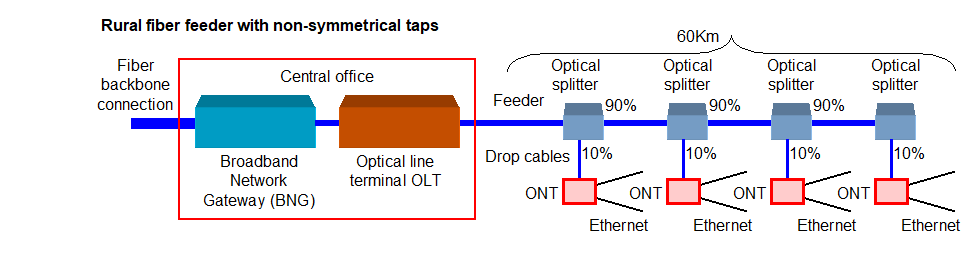
Rural areas present a different challenge for the network designer. In this case homesteads are spread over distances of miles, usually along a highway. One feeder fiber can be installed along the side of the highway with optical splitters installed at points in the cable to connect a fiber drop cable to each homestead. In order to preserve the length of the feeder fiber each optical splitter is asymmetrical so that the tap for the drop cable uses 10% of the optical power while 90% of the optical power connects to the next feeder segment.
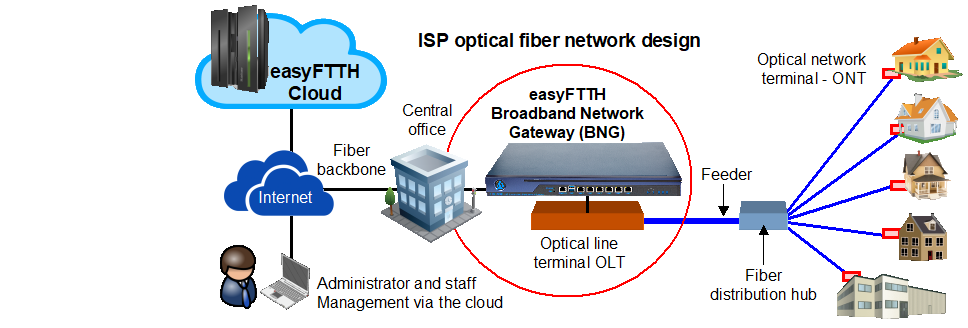
The easyFTTH network access controller is a router that also has data processing capability. It downloads the subscriber database from the cloud and implements access control
authentication and applies each individual subscriber rate plan. The ISP may wish to offer subscribers different data speeds with respective pricing which will help to increase
the contention ratio of the network and hence increase the profitability of the system.
When the ISP network has one central office with one or more fiber distribution hubs the easyFTTH network access controller is installed between the incoming fiber backbone connection
and the optical line terminal (OLT). All subscribers connect to the backbone fiber and are managed by the easyFTTH network access controller.
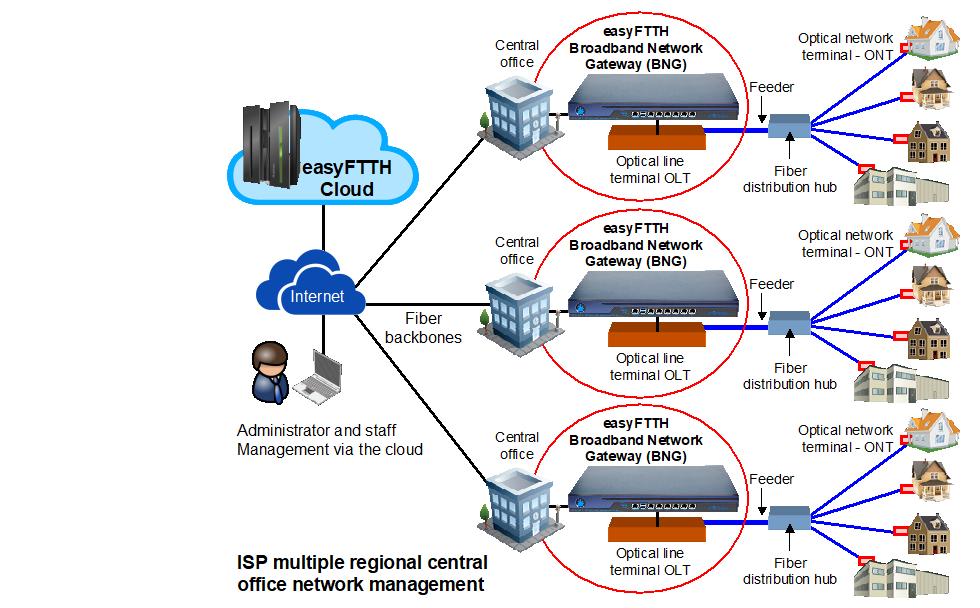
As the ISP expands to cover a larger geography it will be necessary to build several regional central offices each with a backbone fiber connection. An easyFTTH network access controller is installed at each regional central office and all easyFTTH network access controllers are managed transparently by the cloud. It is only necessary to add the name of the regional central office to the new subscribers account.
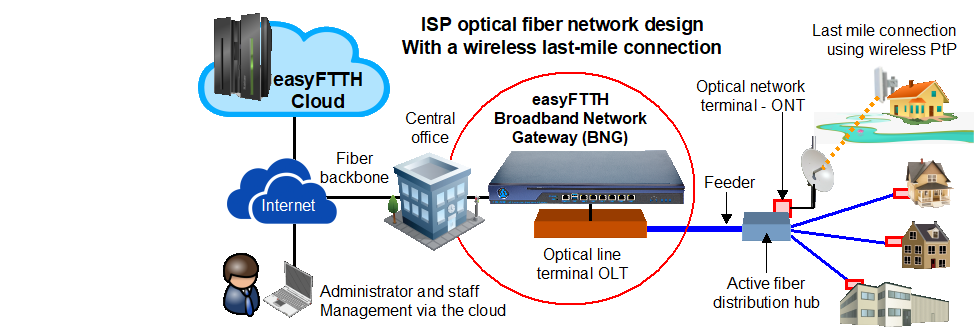
Fiber technology can be mixed with wireless technology. For example, when the last mile of a subscribers network cannot be connected with fiber for a geographic reason (there may be a river between the fiber distribution hub and the subscriber), then a wireless point to point link can be installed from the fiber distribution hub to the home. In this case the fiber distribution hub must be active with power and a backup supply to power the ONT and the wireless access point. Point to point wireless links are available up to 1Gb/s.
The easyFTTH Broadband Network Gateway (BNG) and Cloud technology offer a series of advantages for both new and established ISPs by dramatically reducing the investment and operating costs of implementing management systems compared with any other technical solution. By reducing the technical complexity it is possible for a person with limited technical skills and financial resources to start a ISP business. ISP entrepreneurs can accelerate the time to service deployment and initiate revenue generation earlier in the startup cycle.